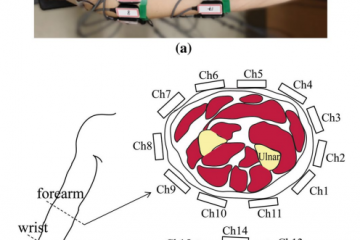
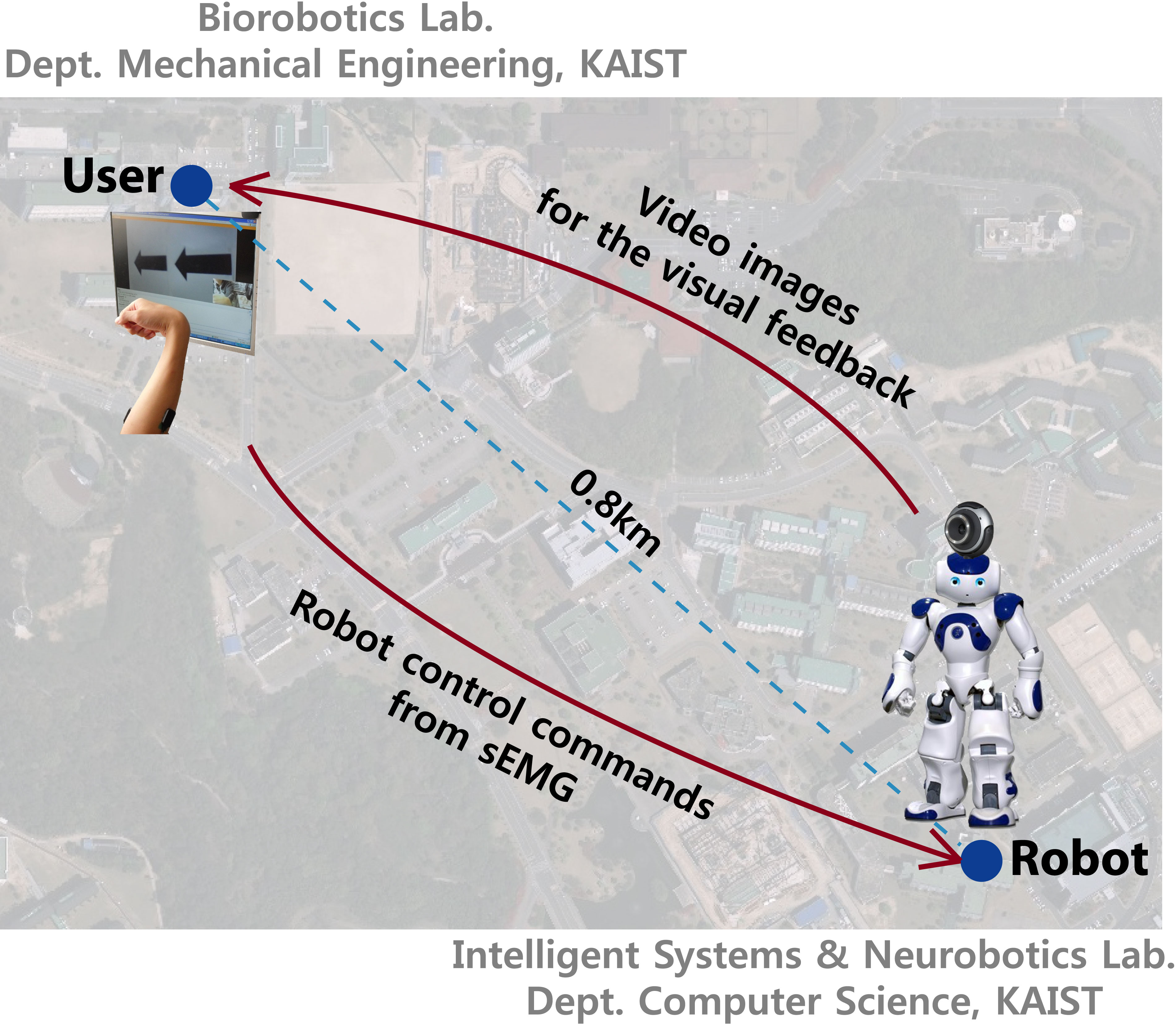
This paper presents an application of noninvasive sEMG-based interface to humanoid robot navigation control between remote places via wireless internet communication. sEMG signals to recognize three wrist movements are measured from the skin of a uses arm. The wrist movements generate commands to the humanoid robot. The wrist movement directions are assigned to be intuitively comparable with the robot movement directions, therefore a user can control the robot in a natural way. By combining the state automation machine to the sEMG-based interface, possible robot movements are extended. To provide the environmental information of remote places, the images from the camera on the robots head are transmitted into the interface PC screen. We conducted experiments in which subjects control a humanoid robot to navigate from a starting position to a destination in a maze. The experimental results demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed interface method by comparing it with the keyboard control.
Related publications
1. Y Chae, C Choi, J Kim, S Jo, Noninvasive sEMG-based control for humanoid robot teleoperated navigation, International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 12(6), December 2011. [PDF]